Introduction
As the world transitions towards renewable energy, understanding the various systems that power our homes and businesses is essential. One of the primary distinctions in the energy sector is whether a system is on-grid or off-grid. These terms refer to whether a property is connected to the public electricity grid or operates independently using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the key differences between on-grid and off-grid electricity systems, their respective advantages, disadvantages, and help you determine which system best suits your needs. We’ll also explore how integrating systems like wind turbines and solar panels into both on-grid and off-grid setups can enhance energy independence and sustainability.
What is an On-Grid Electricity System?
Definition of On-Grid Systems
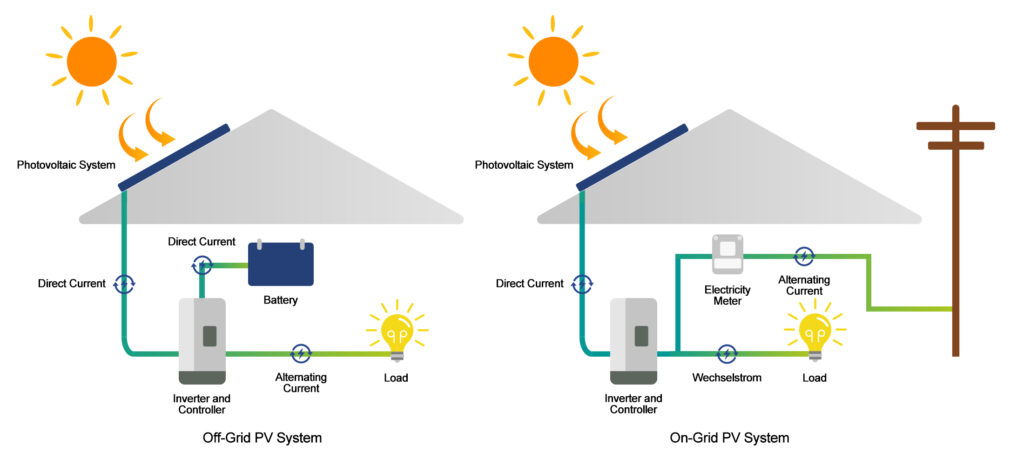
An on-grid electricity system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected system, is connected to the public utility grid. It relies on the electricity provided by the utility company but may also integrate renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines.
In an on-grid system, electricity is drawn from the utility grid when the renewable energy system isn’t generating enough power, and excess power generated by the renewable system is sent back to the grid. This setup allows homeowners to receive credits for the energy they send to the grid, often through a system known as net metering.
How Does On-Grid Electricity Work?
The basic setup of an on-grid system includes the following components:
- Solar panels or wind turbines: These capture renewable energy and convert it into electricity.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC (direct current) electricity from the panels or turbine into AC (alternating current) electricity used by home appliances.
- Utility grid: The utility company provides the electricity to your home when your system isn’t generating enough power.
- Net metering: This allows you to send surplus electricity back to the grid and receive credits, which can be used when your system isn’t generating enough energy.
Advantages of On-Grid Systems
- Cost-Effective: Since on-grid systems rely on the utility grid for backup power, there’s no need to invest in expensive batteries for energy storage.
- Easy to Maintain: Maintenance is generally lower as the system is connected to an established power source (the grid).
- Net Metering: Excess energy generated by your system can be sent back to the grid in exchange for energy credits, which can reduce your overall electricity bill.
- Lower Initial Investment: On-grid systems tend to be more affordable than off-grid systems because they don’t require energy storage solutions (e.g., batteries).
What is an Off-Grid Electricity System?
Definition of Off-Grid Systems
An off-grid electricity system operates independently of the utility grid. It’s typically used in remote areas or for homes and businesses that want to achieve complete energy independence. These systems are powered by renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines, and the electricity generated is stored in batteries for later use.
Off-grid systems are ideal for locations where it’s not feasible or cost-effective to connect to the public utility grid.
How Does Off-Grid Electricity Work?
An off-grid system involves the following components:
- Solar panels or wind turbines: These renewable energy sources generate electricity.
- Batteries: Store the electricity generated for use when renewable energy sources aren’t available (such as at night or on calm days).
- Charge controller: Manages the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the home, ensuring batteries are charged properly and not overcharged.
- Inverter: Converts the DC electricity from the panels or batteries into AC electricity.
Since off-grid systems do not rely on the utility grid, they must be sized to meet the energy needs of the home or business at all times, including during periods of low sunlight or wind.
Advantages of Off-Grid Systems
- Energy Independence: Off-grid systems allow you to produce and consume your own electricity without relying on an external utility company.
- No Monthly Utility Bills: Since you're not connected to the grid, there’s no need to pay monthly electricity bills.
- Ideal for Remote Locations: Off-grid systems are perfect for homes in areas where it’s difficult to establish a connection to the grid, like in rural or isolated locations.
- Sustainable: Off-grid systems promote self-sufficiency and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, providing a more eco-friendly option for sustainable living.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
While both on-grid and off-grid systems provide renewable energy solutions, they differ significantly in terms of cost, maintenance, reliability, and sustainability.
Comparison Table: On-Grid vs. Off-Grid Systems
| Feature | On-Grid Systems | Off-Grid Systems |
| Connection | Connected to the public utility grid | Not connected to the utility grid |
| Energy Storage | No need for batteries (uses grid for backup) | Requires batteries to store excess energy |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, no battery storage needed | Higher upfront cost due to battery installation |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs | Requires more maintenance, especially for batteries |
| Energy Availability | Relies on the grid for backup power | Completely independent; relies on renewable energy and storage |
| Environmental Impact | Low environmental impact (still uses grid) | Zero reliance on fossil fuels, fully sustainable |
| Net Metering | Available in many areas to credit excess power | No net metering; no power goes back to the grid |
| Ideal Use | Urban and suburban areas, easy grid access | Remote or rural areas, complete energy independence |
Benefits of Using Wind and Solar in On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
Hybrid Wind and Solar Systems
A hybrid system that combines both solar panels and wind turbines is ideal for both on-grid and off-grid configurations. By leveraging both sources of renewable energy, you can ensure consistent electricity generation, even when one source is not as effective (e.g., windless days or cloudy periods).
- Solar energy is available during daylight hours, making it perfect for daytime use.
- Wind energy is typically more consistent at night or in seasons when sunlight is limited.
Learn more about Automaxx hybrid wind and solar systems and how they can enhance your home’s energy independence. Explore Hybrid Solutions.
Wind Power vs. Solar Power: Which is Better?
| Factor | Wind Power | Solar Power |
| Energy Availability | More effective in windy areas, day or night | More effective in sunny areas, daytime only |
| Efficiency | Typically less efficient than solar in low wind conditions | Highly efficient in areas with lots of sunlight |
| Maintenance | Requires maintenance of moving parts | Generally lower maintenance |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront cost for installation | Lower initial cost for setup |
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
How to Decide Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
When deciding which system is right for you, consider the following factors:
- Location: If you live in an area with reliable grid access, an on-grid system might be the most cost-effective option. If you're in a remote area with no grid access, an off-grid system may be necessary.
- Budget: On-grid systems typically require a lower initial investment, but off-grid systems may have long-term savings due to the absence of utility bills.
- Energy Needs: Calculate your energy needs to determine the appropriate size of the system. Off-grid systems require larger batteries and more equipment to handle fluctuating energy demands.
- Sustainability Goals: If you’re focused on achieving complete energy independence and reducing your carbon footprint, an off-grid system might align better with your goals.

Explore Automaxx Wind Turbines:
Explore Automaxx Solar Panels:
Environmental Impact of On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
Both on-grid and off-grid systems are environmentally friendly compared to traditional fossil-fuel-based power generation, but there are key differences:
- On-Grid: While on-grid systems provide renewable energy, they still rely on the utility grid for backup, which may include non-renewable energy sources.
- Off-Grid: Off-grid systems provide 100% renewable energy and allow users to be completely independent from fossil fuels.
For more on the environmental impact of wind energy, visit U.S. Department of Energy.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between on-grid and off-grid systems is essential for homeowners, businesses, and anyone interested in adopting renewable energy solutions. While on-grid systems are more affordable and easier to maintain, off-grid systems offer complete independence from the utility grid and provide long-term sustainability.
By incorporating wind turbines, solar panels, or hybrid systems into your energy setup, you can help reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a cleaner environment. Whether you choose on-grid or off-grid, the transition to renewable energy is a step toward a more sustainable future.
For more information on Automaxx Wind Turbines and how they can be integrated into both on-grid and off-grid systems, explore our full range of products and solutions.
FAQ
Q1: What is the main difference between on-grid and off-grid systems?
On-grid systems are connected to the public electricity grid, while off-grid systems operate independently using renewable energy and batteries for storage.
Q2: Which system is more cost-effective?
On-grid systems are typically more affordable initially because they don’t require batteries for storage, but off-grid systems offer complete energy independence.
Q3: Can a hybrid system be used for both on-grid and off-grid setups?
Yes, hybrid systems combining wind and solar are ideal for both on-grid and off-grid solutions, ensuring consistent energy availability.



























