Introduction
Wind energy has become one of the most promising sources of renewable energy. In recent years, residential wind turbines have gained popularity as homeowners look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint, save on energy bills, and contribute to sustainable energy production. With the growing interest in wind power, it's essential to understand the different types of wind turbines available for residential use.
This blog will explore the three main types of residential wind turbines: horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs), vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs), and hybrid systems. We will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each type, their applications, and what homeowners need to consider before investing in a wind turbine.
1. Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs)
What are Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines?
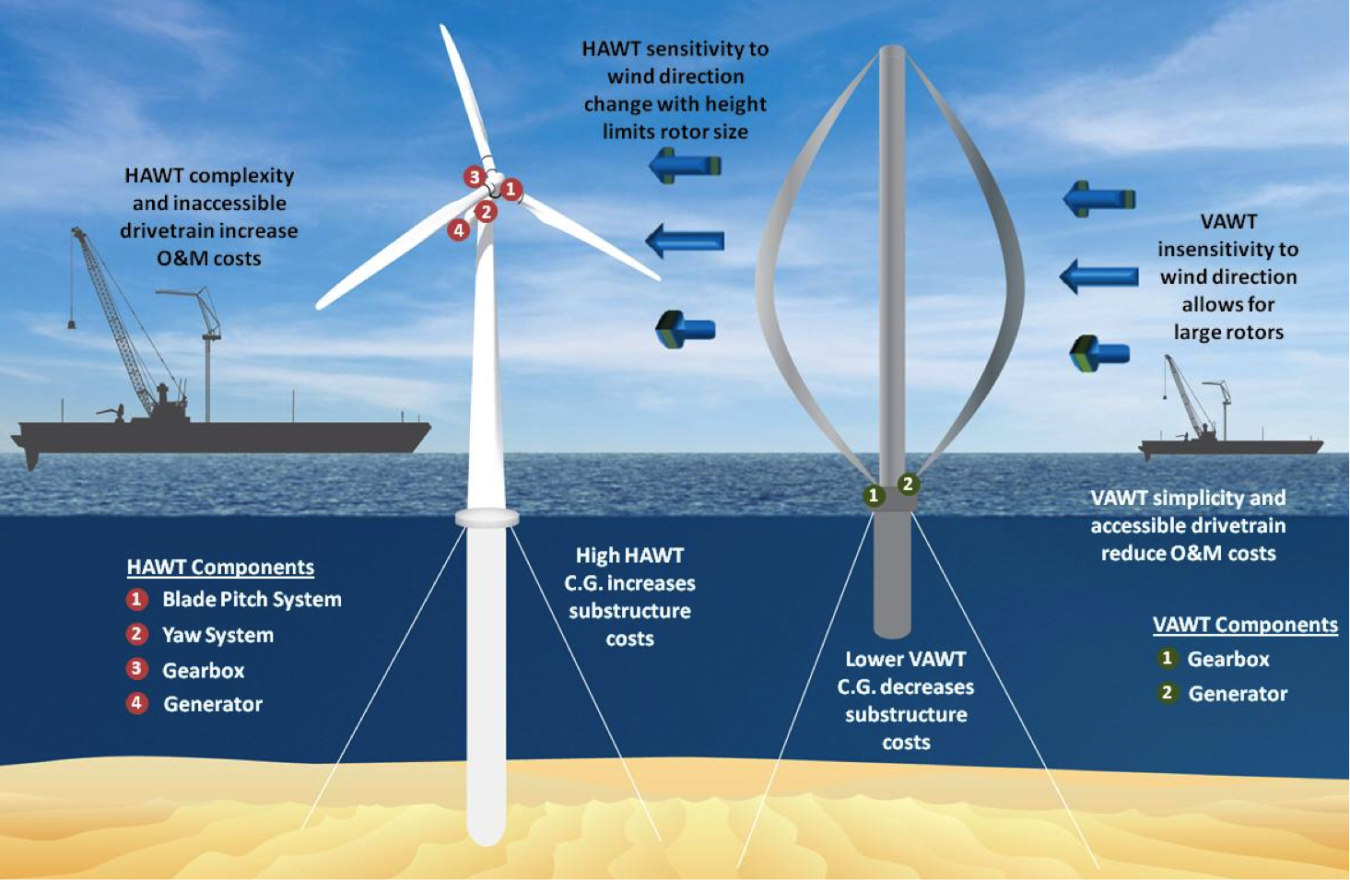
Horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs) are the most common type of wind turbine. These turbines have blades that rotate on a horizontal axis and are designed to face the wind, similar to a traditional windmill. HAWTs are generally more efficient and powerful than other types of turbines, making them suitable for residential areas with consistent wind resources.
How HAWTs Work
HAWTs consist of blades, a hub, a generator, and a tower. The blades are mounted on the hub, which is connected to the generator. The wind causes the blades to rotate, turning the hub and generating electricity. The tower is used to elevate the turbine to a height where it can access stronger winds.
HAWT Components and Function
| Component | Function |
| Blades | Capture wind energy and rotate the hub |
| Hub | Connects blades to the generator |
| Generator | Converts mechanical energy into electricity |
| Tower | Elevates the turbine for optimal wind access |
Advantages of HAWTs
- Higher Efficiency: HAWTs are known for their high energy conversion efficiency because they can capture wind from any direction.
- Proven Technology: HAWTs have been widely used in commercial wind farms and are tested to be reliable and durable.
- Higher Power Output: These turbines generate more power, making them suitable for residential homes with larger energy needs.
Disadvantages of HAWTs
- Higher Initial Cost: HAWTs tend to be more expensive than VAWTs due to their larger size, higher efficiency, and complex setup.
- Space Requirements: HAWTs require more space and need to be installed in areas with unobstructed wind flow. This can be a challenge in urban areas with limited space.
- Maintenance: The moving parts in HAWTs can require more maintenance over time, especially the gearbox and bearings.
2. Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
What are Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines?
Vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have blades that rotate around a vertical axis, which is a significant difference from HAWTs. These turbines are less common but are gaining traction for residential use, especially in areas with lower wind speeds or for homeowners who have limited space.
How VAWTs Work
In VAWTs, the blades are mounted vertically, and the wind forces them to rotate around the vertical axis. The power is generated as the rotor spins. The advantages of VAWTs are that they can capture wind from any direction, unlike HAWTs that must face into the wind. VAWTs are generally simpler in design and are often smaller than HAWTs, which makes them easier to install in urban areas or residential backyards.
Advantages of VAWTs
- Compact Design: VAWTs are smaller and can be installed in tight spaces, making them ideal for residential areas with limited room.
- Wind Direction Independence: These turbines can harness wind from any direction, meaning they do not need to be orientated towards the wind.
- Lower Maintenance: With fewer moving parts compared to HAWTs, VAWTs generally require less maintenance.
Disadvantages of VAWTs
- Lower Efficiency: VAWTs are typically less efficient than HAWTs because their design makes them more susceptible to drag.
- Smaller Power Output: VAWTs generally produce less power than HAWTs, making them more suitable for homes with lower energy needs.
- Noise: While not as common, some VAWTs can create noise due to their design, which may be disruptive in residential areas.
3. Hybrid Wind and Solar Power Systems
What Are Hybrid Wind and Solar Power Systems?
A hybrid wind and solar power system combines both solar panels and wind turbines to generate energy. These systems take advantage of the strengths of both solar and wind power, providing a more consistent and reliable energy source. Solar energy is often generated during the day, while wind energy can be harnessed at night or during cloudy conditions, providing a continuous energy supply.
How Hybrid Systems Work
Hybrid systems are typically connected to the grid, but they can also be used as off-grid solutions. The solar panels capture sunlight during the day and convert it into electricity, while the wind turbines generate power when wind conditions are favorable. The energy generated by both systems is stored in batteries or fed back into the grid.
Comparison of Hybrid Wind and Solar Power System Benefits
| Benefit | Wind Energy | Solar Energy | Hybrid System |
| Energy Availability | Available during day and night | Available during the day | Available 24/7, more reliable |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Low to moderate cost | Higher initial cost, long-term savings |
| Efficiency | High in windy areas | High in sunny areas | Increased efficiency in varied conditions |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance |
Advantages of Hybrid Systems
- Higher Energy Reliability: Hybrid systems provide more consistent power generation by combining two renewable sources.
- Reduced Dependency on the Grid: Hybrid systems are ideal for off-grid homes, providing an independent source of energy.
- Increased Power Output: By utilizing both wind and solar, hybrid systems can generate more power compared to individual wind or solar systems.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Systems
- Higher Initial Investment: Hybrid systems require an upfront investment in both solar panels and wind turbines, making them more expensive than single-source systems.
- Complex Installation: Installing a hybrid system is more complex and may require professional help.
- Space Requirements: Both solar panels and wind turbines need space, which may not be available in some residential areas.
How to Choose the Right Wind Turbine for Your Home
Factors to Consider
When deciding which type of wind turbine is best for your home, consider the following factors:
- Wind Resources: The average wind speed in your area will determine which type of wind turbine is most efficient. HAWTs are generally better for areas with strong, consistent winds, while VAWTs are more suitable for areas with variable wind conditions.
- Space Availability: HAWTs require more space for installation, while VAWTs can fit into smaller areas.
- Budget: HAWTs are more expensive than VAWTs, but they also provide higher energy output. Hybrid systems can be the most expensive but offer the best long-term energy solution.

Environmental Impact of Wind Energy
Wind energy is one of the cleanest forms of energy, producing no emissions and minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. However, it’s important to consider the full environmental impact of wind energy systems, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Environmental Benefits of Wind Energy
- Reduces Carbon Emissions: Wind energy does not produce greenhouse gases, helping mitigate climate change.
- Sustainable Resource: Wind is a renewable resource that can be harnessed indefinitely.
- No Water Use: Unlike other energy sources like nuclear or fossil fuel plants, wind energy does not require water for cooling.
Considerations
- Wildlife Impact: Wind turbines can pose a threat to birds and bats. However, new technologies and regulations are being implemented to mitigate these risks.
- Land Use: Large wind farms require significant land area, although residential turbines have minimal impact on land use.
Conclusion
Residential wind turbines provide a sustainable, renewable energy source that can help homeowners reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy costs. By understanding the three main types of wind turbines—horizontal-axis, vertical-axis, and hybrid systems—you can make an informed decision about the best energy solution for your home. Whether you choose a wind turbine, solar panels, or a hybrid system, incorporating renewable energy into your home is a powerful way to contribute to a more sustainable future.
FAQ
Q1: How long do wind turbines last?
Most wind turbines have a lifespan of 20-25 years, with proper maintenance and care. The blades and generators may need to be replaced after this period.
Q2: Do I need a permit to install a residential wind turbine?
Yes, in many regions, you will need a permit for installing a residential wind turbine. It’s important to check local zoning laws and regulations before proceeding with installation.
Q3: Can I install a hybrid wind and solar system?
Yes, hybrid systems are increasingly popular for homeowners looking for a reliable and consistent energy solution. They combine both wind turbines and solar panels, ensuring energy availability day and night.










